Student exploration fast plants 1 growth and genetics – Student Exploration: Fast Plants Growth and Genetics delves into the captivating world of plant biology, offering a comprehensive exploration of the unique characteristics and applications of fast-growing plants in educational settings and beyond.
Fast plants, known for their rapid growth and short life cycles, provide an ideal platform for students to investigate fundamental concepts in plant science. This guide will explore the benefits and limitations of using fast plants in educational contexts, showcase innovative student experiments and projects, and delve into the genetic basis of fast plant growth and development.
Student Exploration: Fast Plants Growth
Fast plants are small, rapidly growing plants that are ideal for use in student exploration of plant biology. They have a short life cycle of just 2-3 weeks, making it possible to complete multiple generations of plants in a single semester.
Fast plants are also easy to grow and require minimal care, making them a good choice for students of all ages.
Benefits of Using Fast Plants for Educational Purposes
- Short life cycle allows for multiple generations of plants in a single semester.
- Easy to grow and require minimal care.
- Well-suited for genetic studies due to their rapid generation time and large population size.
- Can be used to demonstrate a wide range of plant biology concepts, including genetics, growth, and development.
Limitations of Using Fast Plants for Educational Purposes
- Small size may limit their use for some experiments.
- Not all plant biology concepts can be demonstrated using fast plants.
- Can be difficult to obtain seeds for some varieties.
Examples of Student Experiments and Projects Involving Fast Plants
- Investigating the effects of environmental factors on plant growth.
- Studying the genetics of plant growth and development.
- Developing new fast plant varieties.
- Using fast plants to teach students about plant biology.
Genetics of Fast Plants
The genetic basis of fast plant growth and development is complex and involves multiple genes. However, several key genes have been identified that play a role in regulating plant growth rate.
Key Genes and Mutations that Influence Plant Growth Rate
- FTgene: Encodes a protein that promotes flowering. Mutations in this gene can lead to early flowering and reduced plant size.
- FLCgene: Encodes a protein that represses flowering. Mutations in this gene can lead to late flowering and increased plant size.
- GA1gene: Encodes a protein that is involved in gibberellin biosynthesis. Gibberellins are plant hormones that promote stem elongation and leaf growth.
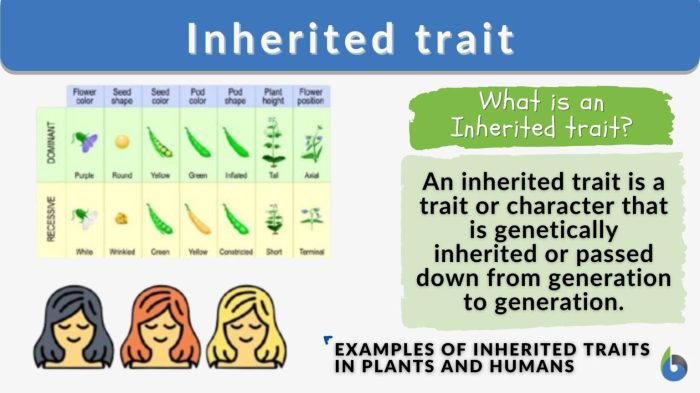
Genetic Variation Contributes to Phenotypic Diversity in Fast Plants
Genetic variation among fast plant varieties contributes to phenotypic diversity in these plants. This variation can be seen in traits such as plant height, leaf size, and flowering time.
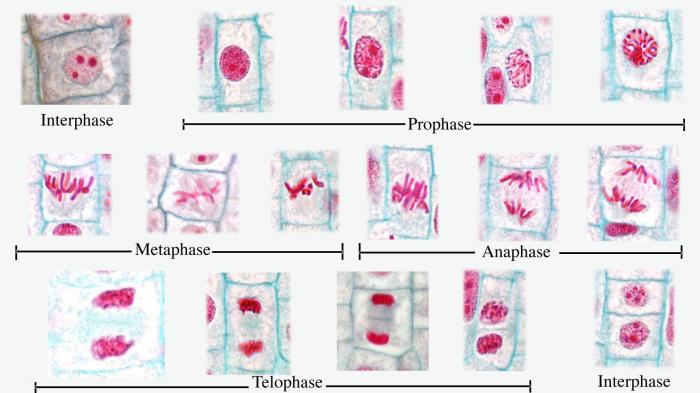
Experimental Design for Fast Plant Studies
When designing an experiment to investigate the effects of environmental factors on fast plant growth, it is important to consider the following variables:
Experimental Variables
- Independent variable: The variable that is being manipulated by the experimenter.
- Dependent variable: The variable that is being measured by the experimenter.
- Controlled variables: Variables that are kept constant throughout the experiment.
Controls
It is important to include controls in an experiment to ensure that the results are valid. Controls allow the experimenter to compare the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable while eliminating the effects of other variables.
Data Collection Methods
There are a variety of methods that can be used to collect data in fast plant studies. These methods include:
- Measuring plant height
- Counting leaves
- Measuring leaf area
- Recording flowering time
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Once data has been collected, it is important to analyze the data to determine if there is a significant effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. Statistical methods can be used to analyze the data and determine if there is a statistically significant difference between the treatment groups.
Interpreting the Results of Experiments, Student exploration fast plants 1 growth and genetics
When interpreting the results of experiments, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The magnitude of the effect
- The statistical significance of the effect
- The biological significance of the effect
Applications of Fast Plant Research
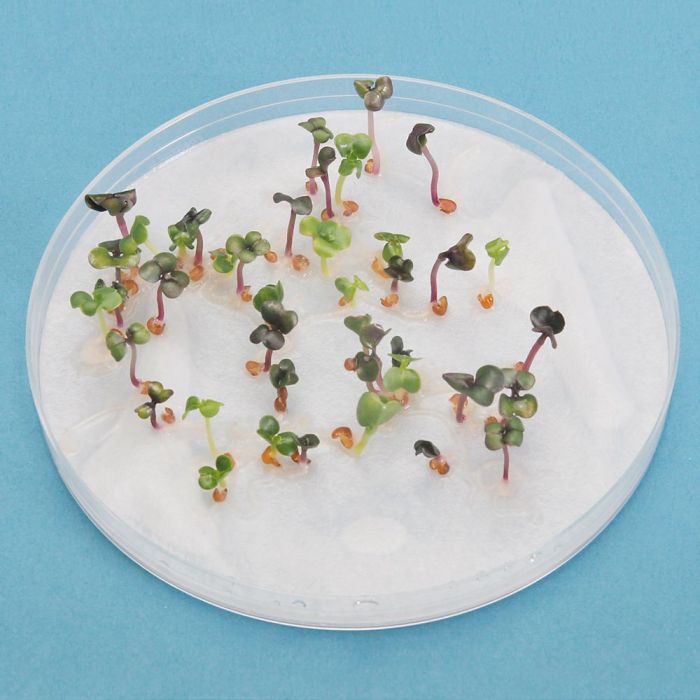

Fast plant research has a wide range of applications in agriculture, horticulture, and plant breeding. Fast plants can be used to:
Applications in Agriculture
- Develop new crop varieties with improved yield and quality.
- Identify genes that control important agronomic traits.
- Study the effects of environmental factors on plant growth and development.
Applications in Horticulture
- Develop new ornamental plants with improved appearance and performance.
- Study the effects of environmental factors on plant growth and development.
- Identify genes that control important horticultural traits.
Applications in Plant Breeding
- Develop new plant varieties with improved yield, quality, and resistance to pests and diseases.
- Identify genes that control important plant breeding traits.
- Study the effects of environmental factors on plant growth and development.
Detailed FAQs: Student Exploration Fast Plants 1 Growth And Genetics
What are the advantages of using fast plants in education?
Fast plants offer several advantages in education, including their rapid growth rate, which allows for multiple generations to be studied within a short time frame; their small size, which makes them suitable for classroom environments; and their ease of cultivation, which minimizes resource requirements.
How can fast plants contribute to genetic research?
Fast plants have played a significant role in genetic research due to their short generation time and large population sizes. They have been used to identify genes and mutations that influence plant growth and development, and to study the genetic basis of phenotypic diversity.
What practical applications do fast plants have in agriculture and horticulture?
Fast plants have practical applications in agriculture and horticulture. They can be used to screen for desirable traits, such as disease resistance or drought tolerance, and to develop new crop varieties with improved yield and quality.