Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells worksheet answer key pdf – Unveiling the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, this comprehensive worksheet answer key PDF serves as an invaluable guide for students and educators alike. Delving into the intricate structures, functions, and evolutionary significance of these microscopic marvels, this resource provides a deeper understanding of the building blocks of life.
Through detailed comparisons and engaging explanations, this worksheet answer key sheds light on the distinct characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, empowering learners to grasp the complexities of cellular biology and appreciate the diversity of life on Earth.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
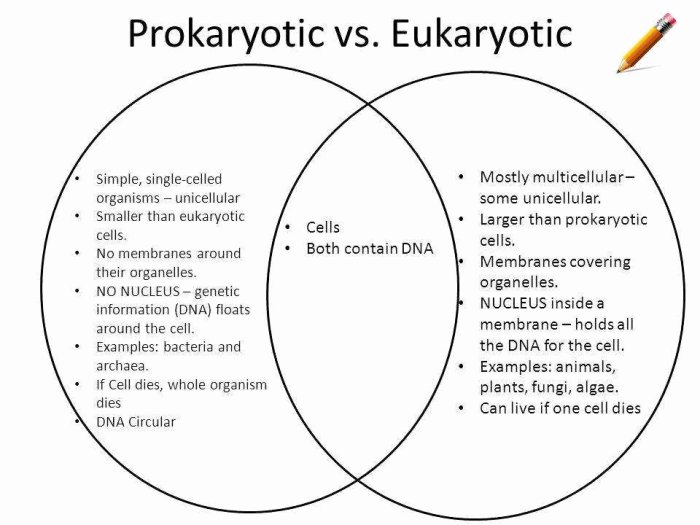
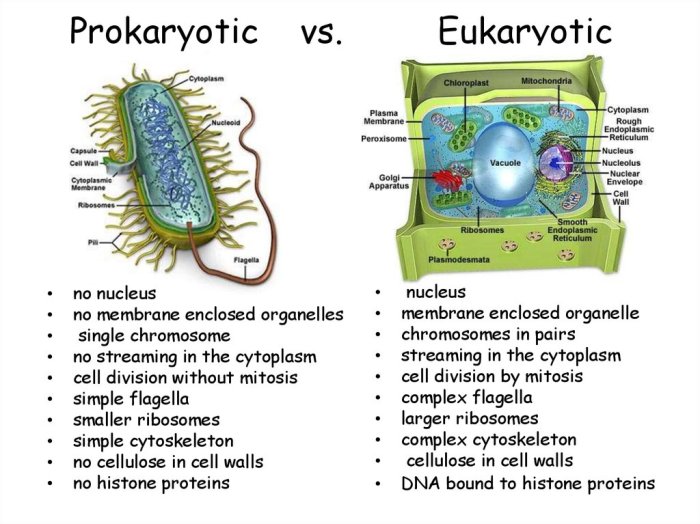
Cells are the basic units of life, and they come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and they lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, and they are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells.
Key Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
The following table summarizes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Cell size | Typically 0.1-5.0 micrometers | Typically 10-100 micrometers |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Have membrane-bound organelles |
| DNA structure | Circular DNA | Linear DNA |
| Cell division | Binary fission | Mitosis or meiosis |
Detailed Comparison of Cell Structures
Prokaryotic cells are typically much smaller than eukaryotic cells, and they have a simpler structure. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their DNA is located in a region of the cell called the nucleoid.
Prokaryotic cells also have ribosomes, which are small structures that produce proteins.
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells, and they have a larger size. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA. Eukaryotic cells also have other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus.
These organelles perform specific functions that are essential for the cell’s survival.
Functions and Adaptations of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of environments, including extreme environments such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Prokaryotic cells are also found in the human body, where they play a role in digestion and other bodily functions.
Eukaryotic cells are found in all multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells are also found in some single-celled organisms, such as yeast. Eukaryotic cells are able to perform a wider range of functions than prokaryotic cells, and they are more complex and specialized.
Evolution and Significance of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells worksheet answer key pdf
Prokaryotic cells are thought to be the first cells to evolve on Earth. Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells about 2 billion years ago. The evolution of eukaryotic cells was a major event in the history of life on Earth, and it allowed for the development of more complex and diverse organisms.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells play a vital role in the biosphere. Prokaryotic cells are responsible for cycling nutrients through the environment, and they are also involved in the production of oxygen and other gases. Eukaryotic cells are responsible for a wide range of functions, including photosynthesis, respiration, and reproduction.
FAQ: Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The presence of a nucleus is the key difference, with eukaryotic cells possessing a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells lacking one.
How do prokaryotic cells divide?
Prokaryotic cells divide through binary fission, a simple process where the cell splits into two identical daughter cells.
What are the functions of eukaryotic cell organelles?
Organelles perform specialized functions within eukaryotic cells, such as energy production (mitochondria), protein synthesis (ribosomes), and material transport (endoplasmic reticulum).