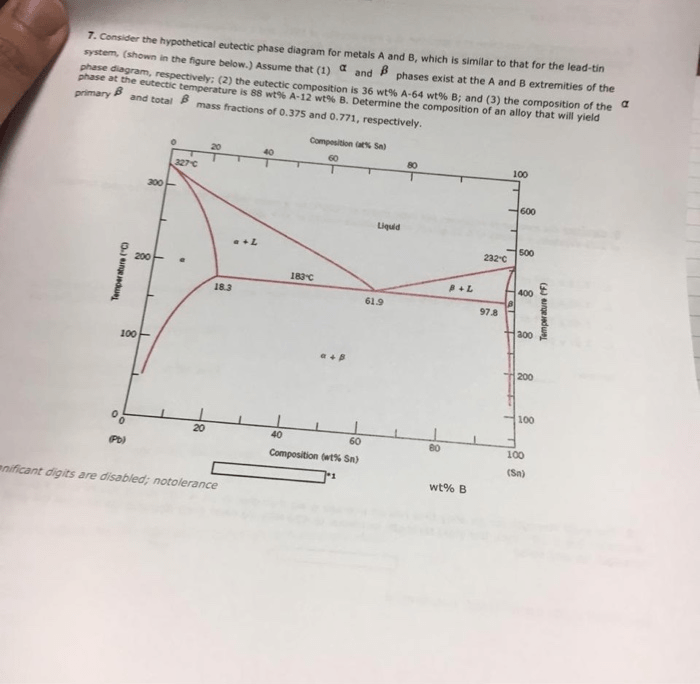
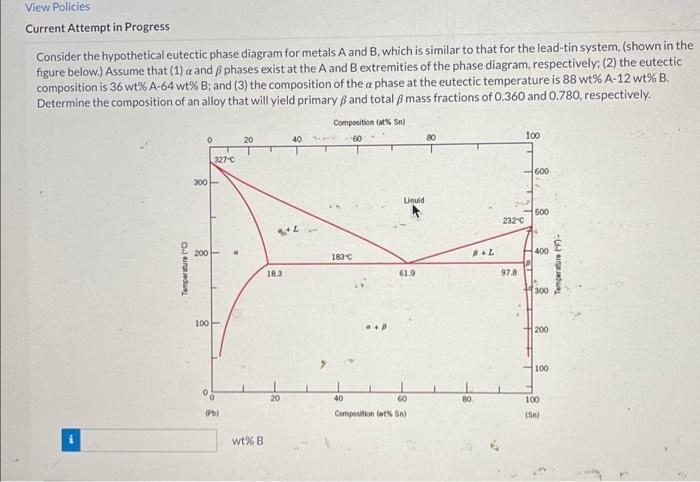
Consider the hypothetical eutectic phase diagram, a foundational concept in materials science and engineering, as we delve into its intricacies. This diagram serves as a graphical representation of the equilibrium states of a system, providing valuable insights into the solidification and melting behavior of materials.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the fundamental principles that govern these diagrams and their far-reaching applications.
Eutectic phase diagrams are characterized by a unique point known as the eutectic point, which represents the lowest melting temperature of the system. This point is crucial in understanding the solidification process, as it determines the formation of specific microstructures and the properties of the resulting material.
1. Phase Diagram Basics
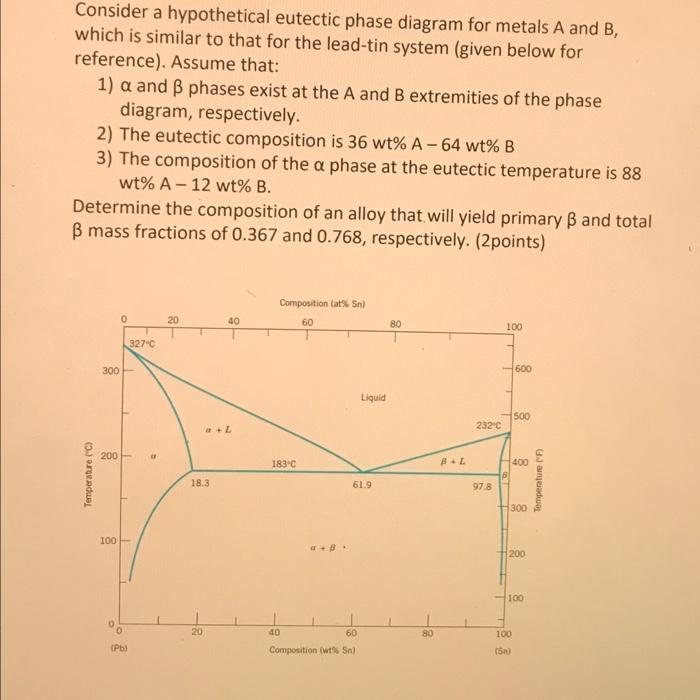
Phase diagrams are graphical representations that depict the thermodynamic conditions under which different phases of a substance exist. They provide valuable insights into the behavior of materials and are widely used in materials science and engineering.
There are various types of phase diagrams, including unary, binary, and ternary phase diagrams. Unary phase diagrams represent a single component system, while binary phase diagrams represent a two-component system, and ternary phase diagrams represent a three-component system. Each type of phase diagram has its own applications and provides information about the phases present at different temperatures and compositions.
The eutectic phase diagram is a specific type of binary phase diagram that describes the behavior of a system with two components that form a eutectic mixture. Eutectic mixtures have a unique composition and melting point that is lower than the melting point of either of the pure components.
2. Eutectic Phase Diagram Characteristics
The eutectic phase diagram is characterized by the presence of a eutectic point, which represents the lowest melting temperature of the system. The eutectic point is located on the liquidus and solidus lines, which represent the temperatures at which the liquid and solid phases start to form, respectively.
The eutectic phase diagram is divided into different regions, each representing a different phase or combination of phases. These regions include the liquid region, the solid region, and the two-phase region, where both the liquid and solid phases coexist.
3. Applications of Eutectic Phase Diagrams
Eutectic phase diagrams have numerous applications in materials science and engineering. They are used to design alloys with specific properties, such as high strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
For example, the eutectic phase diagram of the aluminum-silicon system is used to design alloys for casting applications. The eutectic composition in this system has a low melting point and excellent fluidity, making it suitable for casting complex shapes.
4. Limitations and Extensions, Consider the hypothetical eutectic phase diagram
Eutectic phase diagrams have limitations and may not be applicable in all situations. For example, they do not account for the effects of pressure or magnetic fields.
To overcome these limitations, extensions to eutectic phase diagrams have been developed, such as ternary and quaternary phase diagrams. These extensions consider additional components and provide more complex and accurate representations of real-world systems.
Key Questions Answered: Consider The Hypothetical Eutectic Phase Diagram
What is the significance of the eutectic point in a phase diagram?
The eutectic point represents the lowest melting temperature of the system, where two or more phases coexist in equilibrium. It is crucial for understanding the solidification process and the formation of specific microstructures.
How are eutectic phase diagrams used in materials design?
Eutectic phase diagrams guide the design of alloys with specific properties. By controlling the composition and cooling rate, engineers can manipulate the solidification process to achieve desired microstructures and enhance material performance.
What are the limitations of eutectic phase diagrams?
Eutectic phase diagrams are limited to binary systems and assume equilibrium conditions. They may not accurately represent systems with complex compositions or non-equilibrium solidification processes.